Wiliam Osler Y La Neumonia Pdf
Finalmente, al hablar de Sir William Osler nos referimos al mdico que puso las bases para el desarrollo de la medicina actual, y no solo en el campo cientfico, sino tambin en la relacin mdico-paciente.(1) II. Vida y obra Sir William Osler naci el 12 de Julio de 1849 en la poblacin de Bond Head, provincia de Ontario.
BtFRSFRCP | |
|---|---|
| Born | July 12, 1849 Bond Head, Province of Canada |
| Died | December 29, 1919 (aged 70) |
| Residence | Canada United Kingdom |
| Nationality | Canadian |
| Alma mater | McGill University |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | physician, pathologist, internist, educator, bibliophile, author and historian |
| Institutions | |
| Signature | |
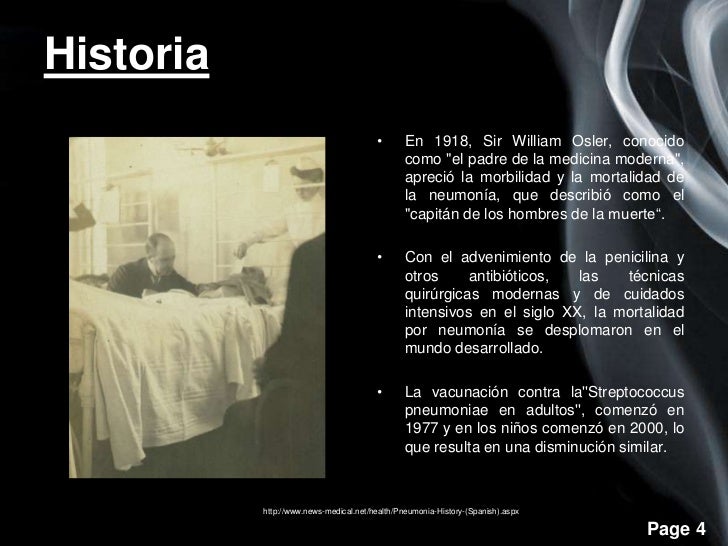
Sir William Osler, 1st Baronet, FRSFRCP (/ˈɒzlər/; July 12, 1849 – December 29, 1919) was a Canadianphysician and one of the four founding professors of Johns Hopkins Hospital. Osler created the first residency program for specialty training of physicians, and he was the first to bring medical students out of the lecture hall for bedside clinical training.[1] He has frequently been described as the Father of Modern Medicine and one of the 'greatest diagnosticians ever to wield a stethoscope'.[2][3] Osler was a person of many interests, who in addition to being a physician, was a bibliophile, historian, author, and renowned practical joker. One of his achievements was the founding of the History of Medicine Society (previously section) of the Royal Society of Medicine, London.[4]
- 1Biography
- 5Eponyms
Biography[edit]
Family[edit]
Causas De La Neumonia
William's great-grandfather, Edward Osler, was variously described as either a merchant seaman or a pirate.[5] One of William's uncles (Edward Osler (1798–1863)), a medical officer in the Royal Navy, wrote the Life of Lord Exmouth and the poem The Voyage. (Osler, Edward, 1798–1863. Lg sound systems for home. The Voyage : a poem, written at sea, and in the West Indies, and illustrated by papers on natural history. London : Longman, 1830). William Osler's father, Featherstone Lake Osler (1805–1895), the son of a shipowner at Falmouth, Cornwall, was a former Lieutenant in the Royal Navy who served on HMS Victory. In 1831 Featherstone Osler was invited to serve on HMS Beagle as the science officer on Charles Darwin's historic voyage to the Galápagos Islands, but he turned it down because his father was dying. In 1833, Featherstone Osler announced he wanted to become a minister of the Church of England.[6]
As a teenager, Featherstone Osler was aboard HMS Sappho when it was nearly destroyed by Atlantic storms and left adrift for weeks. Serving in the Navy, he was shipwrecked off Barbados. In 1837 Featherstone Osler officially retired from the Navy and emigrated to Canada, becoming a 'saddle-bag minister' in rural Upper Canada. When Featherstone Osler and his bride, Ellen Free Picton, arrived in Canada, they were nearly shipwrecked again on Egg Island in the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. The Oslers had several children, including William, Britton Bath Osler, and Sir Edmund Boyd Osler.
Early life[edit]
William Osler was born in Bond Head, Canada West (now Ontario) on July 12, 1849, and raised after 1857 in Dundas, Ontario. (He was called William after William of Orange, who won the Battle of the Boyne on July 12, 1690.) His mother, who was very religious, prayed that Osler would consecrate to God's service and, in 1867, her son announced he would follow his father's footsteps into the ministry.[7] He was educated at Trinity College School (then located in Weston, Ontario) and entered Trinity College, Toronto (now part of the University of Toronto) in the autumn of 1867.
At the time, however, he was becoming increasingly interested in medical science, under the influence of James Bovell, and Rev. William Arthur Johnson, who both became major influences for Osler at this time, encouraging him to switch his career.[8][9][10] In 1868, Osler enrolled in the Toronto School of Medicine,[11] a privately owned institution, not part of the Medical Faculty of the University of Toronto. Osler lived with Bovell for a time, and through Johnson, he was introduced to the writings of Sir Thomas Browne; his Religio Medici caused a deep impression on him.[12] Osler left the Toronto School of Medicine after being accepted to the MDCM program at McGill University Faculty of Medicine in Montreal and he received his medical degree (MDCM) in 1872.
Career[edit]
Following post-graduate training under Rudolf Virchow in Europe, Osler returned to the McGill University Faculty of Medicine as a professor in 1874. Here he created the first formal journal club. During this time, he also showed interest in comparative pathology and is considered the first to teach veterinary pathology in North America as part of a broad understanding of disease pathogenesis. In 1884, he was appointed Chair of Clinical Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia and in 1885, was one of the seven founding members of the Association of American Physicians, a society dedicated to 'the advancement of scientific and practical medicine.' When he left Philadelphia in 1889, his farewell address, 'Aequanimitas',[13] was on the imperturbability (calm amid storm) and equanimity (moderated emotion, tolerance) necessary for physicians.[14]
In 1889, he accepted the position as the first Physician-in-Chief of the new Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, Maryland. Shortly afterwards, in 1893, Osler was instrumental in the creation of the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and became one of the school's first professors of medicine. Osler quickly increased his reputation as a clinician, humanitarian, and teacher. He presided over a rapidly expanding domain. In the hospital's first year of operation, when it had 220 beds, 788 patients were seen for a total of over 15,000 days of treatment. Sixteen years later, when Osler left for Oxford, over 4,200 patients were seen for a total of nearly 110,000 days of treatment.[15]
In 1905, he was appointed to the Regius Chair of Medicine at Oxford, which he held until his death. He was also a Student (Fellow) of Christ Church, Oxford.
In 1911, he initiated the Postgraduate Medical Association, of which he was the first President.[16] In the same year, Osler was named a baronet in the Coronation Honours List for his contributions to the field of medicine.[17]
The largest collection of Osler's letters and papers is at the Osler Library of McGill University in Montreal and a collection of his papers is also held at the United States National Library of Medicine in Bethesda, Maryland.[18][19]
Assessment[edit]
Perhaps Osler's greatest influence on medicine was to insist that students learn from seeing and talking to patients and the establishment of the medical residency. The latter idea spread across the English-speaking world and remains in place today in most teaching hospitals. Through this system, doctors in training make up much of a teaching hospital's medical staff. The success of his residency system depended, in large part, on its pyramidal structure with many interns, fewer assistant residents and a single chief resident, who originally occupied that position for years. While at Hopkins, Osler established the full-time, sleep-in residency system whereby staff physicians lived in the administration building of the hospital. As established, the residency was open-ended, and long tenure was the rule. Doctors spent as long as seven or eight years as residents, during which time they led a restricted, almost monastic life.
He wrote in an essay 'Books and Men' that 'He who studies medicine without books sails an uncharted sea, but he who studies medicine without patients does not go to sea at all.'[20] His best-known saying was 'Listen to your patient, he is telling you the diagnosis,' which emphasises the importance of taking a good history.[2]
The contribution to medical education of which he was proudest was his idea of clinical clerkship – having third- and fourth-year students work with patients on the wards. He pioneered the practice of bedside teaching, making rounds with a handful of students, demonstrating what one student referred to as his method of 'incomparably thorough physical examination.' Soon after arriving in Baltimore, Osler insisted that his medical students attend at bedside early in their training. By their third year they were taking patient histories, performing physicals and doing lab tests examining secretions, blood and excreta.
From left to right: William Henry Welch, William Stewart Halsted, William Osler, Howard Kelly
He reduced the role of didactic lectures and once said he hoped his tombstone would say only, 'He brought medical students into the wards for bedside teaching.' He also said, 'I desire no other epitaph … than the statement that I taught medical students in the wards, as I regard this as by far the most useful and important work I have been called upon to do.' Osler fundamentally changed medical teaching in North America, and this influence, helped by a few such as the Dutch internistP.K. Pel, spread to medical schools across the globe.
Osler was a prolific author and a great collector of books and other material relevant to the history of medicine. He willed his library to the Faculty of Medicine of McGill University where it now forms the nucleus of McGill University's Osler Library of the History of Medicine, which opened in 1929. The printed and extensively annotated catalogue of this donation is entitled 'Bibliotheca Osleriana: a catalogue of books illustrating the history of medicine and science, collected, arranged and annotated by Sir William Osler, Bt. and bequeathed to McGill University'.[21] Osler was a strong supporter of libraries and served on the library committees at most of the universities at which he taught and was a member of the Board of Curators of the Bodleian Library in Oxford. He was instrumental in founding the Medical Library Association in North America, alongside employee and mentee Marcia Croker Noyes,[22] and served as its second president from 1901–1904. In Britain he was the first (and only) president of the Medical Library Association of Great Britain and Ireland[23] and also a president of the Bibliographical Society of London (1913).[24]
Osler was a prolific author and public speaker and his public speaking and writing were both done in a clear, lucid style. His most famous work, 'The Principles and Practice of Medicine' quickly became a key text to students and clinicians alike. It continued to be published in many editions until 2001 and was translated into many languages.[25][26] It is notable in part for supporting the use of bloodletting as recently as 1923.[27] Though his own textbook was a major influence in medicine for many years, Osler described Avicenna as the 'author of the most famous medical textbook ever written'. He noted that Avicenna's Canon of Medicine remained 'a medical bible for a longer time than any other work'.[28]Osler's essays were important guides to physicians. The title of his most famous essay, 'Aequanimitas', espousing the importance of imperturbability, is the motto on the Osler family crest and is used on the Osler housestaff tie and scarf at Hopkins.

Controversy[edit]
Osler is well known in the field of gerontology for the speech he gave when leaving Hopkins to become the Regius Professor of Medicine at Oxford. 'The Fixed Period', given on February 22, 1905, included some controversial words about old age. Osler, who had a well-developed humorous side to his character, was in his mid-fifties when he gave the speech and in it he mentioned Anthony Trollope's The Fixed Period (1882), which envisaged a college where men retired at 67 and after being given a year to settle their affairs, would be 'peacefully extinguished by chloroform'. He claimed that, 'the effective, moving, vitalizing work of the world is done between the ages of twenty-five and forty' and it was downhill from then on.[29] Osler's speech was covered by the popular press which headlined their reports with 'Osler recommends chloroform at sixty'. The concept of mandatory euthanasia for humans after a 'fixed period' (often 60 years) became a recurring theme in 20th century imaginative literature—for example, Isaac Asimov's 1950 novel Pebble in the Sky. In the 3rd edition of his Textbook, he also coined the description of pneumonia as 'the old man's friend' since it allowed elderly individuals a quick, comparatively painless death. Coincidentally, Osler himself died of pneumonia.
Personal life and family[edit]
An inveterate prankster, he wrote several humorous pieces under the pseudonym 'Egerton Yorrick Davis', even fooling the editors of the Philadelphia Medical News into publishing a report on the extremely rare phenomenon of penis captivus, on December 13, 1884.[30] The letter was apparently a response to a report on the phenomenon of vaginismus reported three weeks previously in the Philadelphia Medical News by Osler's colleague Theophilus Parvin.[31] Davis, a prolific writer of letters to medical societies, purported to be a retired U.S. Army surgeon living in Caughnawaga, Quebec (now Kahnawake), author of a controversial paper on the obstetrical habits of Native American tribes that was suppressed and unpublished. Osler would enhance Davis's myth by signing Davis's name to hotel registers and medical conference attendance lists; Davis was eventually reported drowned in the Lachine Rapids in 1884.[31]
Throughout his life, Osler was a great admirer of the 17th century physician and philosopher Sir Thomas Browne.
He died at the age of 70, on December 29, 1919 in Oxford, during the Spanish influenza epidemic, most likely of complications from undiagnosed bronchiectasis.[32] His wife, Grace, lived another nine years but succumbed to a series of strokes. Sir William and Lady Osler's ashes now rest in a niche in the Osler Library at McGill University. They had two sons, one of whom died shortly after birth. The other, Edward Revere Osler, was mortally wounded in combat in World War I at the age of 21, during the 3rd battle of Ypres (also known as the battle of Passchendaele). At the time of his death in August 1917, he was a second lieutenant in the (British) Royal Field Artillery;[33] Lt. Osler's grave is in the Dozinghem Military Cemetery in West Flanders, Belgium.[34] According to one biographer, Osler was emotionally crushed by the loss; he was particularly anguished by the fact that his influence had been used to procure a military commission for his son, who had mediocre eyesight.[35] Lady Osler (Grace Revere) was born in Boston in 1854; her paternal great-grandfather was Paul Revere.[36] In 1876, she married Samuel W. Gross, chairman of surgery at Jefferson Medical College in Philadelphia. Gross died in 1889 and in 1892 she married William Osler who was then professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University.
Osler was a founding donor of the American Anthropometric Society, a group of academics who pledged to donate their brains for scientific study. Osler's brain was taken to the Wistar Institute in Philadelphia to join the Wistar Brain Collection. In April 1987 it was taken to the Mütter Museum, on 22nd Street near Chestnut in Philadelphia where it was displayed during the annual meeting of the American Osler Society.[37][38]
In 1925, a biography of William Osler was written by Harvey Cushing,[39] who received the 1926 Pulitzer Prize for the work. A later biography by Michael Bliss was published in 1999.[35] In 1994 Osler was inducted into the Canadian Medical Hall of Fame.[40]
Eponyms[edit]
Osler lent his name to a number of diseases, signs and symptoms, as well as to a number of buildings that have been named for him.[41][42]
Conditions[edit]
- Osler's sign is an artificially high systolic blood pressure reading due to the calcification of atheroscleroticarteries
- Osler's nodes are raised tender nodules on the pulps of fingertips or toes, an autoimmune vasculitis that is suggestive of subacute bacterial endocarditis. They are usually painful, as opposed to Janeway lesions which are due to emboli and are painless.
- Osler–Weber–Rendu disease (also known as hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia) is a syndrome of multiple vascular malformations on the skin, in the nasal and oral mucosa, in the lungs and elsewhere.
- Osler–Vaquez disease (also known as Polycythemia vera)
- Osler–Libman–Sacks syndrome is an atypical, verrucous, nonbacterial, valvular and mural endocarditis. Final stage of systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Osler's manoeuvre: in pseudohypertension, the blood pressure as measured by the sphygmomanometer is artificially high because of arterial wall calcification. Osler's manoeuvre takes a patient who has a palpable, although pulseless, radial artery while the blood pressure cuff is inflated above systolic pressure; thus they are considered to have 'Osler's sign.'
- Osler's rule: States that a neurological defect has to be related to a specific lesion, in contrast to Hickam's dictum, which states that the neurological defect can be due to several lesions.
- Osler's syndrome is a syndrome of recurrent episodes of colic pain, with typical radiation to back, cold shiverings and fever; due to the presence in Vater's diverticulum of a free-moving gallstone which is larger than the orifice.
- Osler's triad: association of pneumonia, endocarditis, and meningitis.
- Sphryanura osleri is a trematode worm found in the gills of a newt.
- Oslerus osleri is a metastrongyloid nematode lungworm parasite of wild and domestic canids. Osler discovered the parasite while teaching comparative pathology at McGill.
Buildings[edit]
- Osler Building at The Johns Hopkins Hospital currently The Johns Hopkins Hospital Human Resources. Until 2012 the Medical Intensive Care Unit (MICU) was located on the 7th floor.
- Sir William Osler Elementary School – Elementary School in Vancouver, British Columbia
- Ecole Sir William Osler School –Elementary School Winnipeg, Manitoba
- Sir William Osler Elementary School – HWDSB Elementary School in Dundas, Ontario.
- Sir William Osler High School,[43]Toronto, Ontario
- Sir William Osler Public School[44]Simcoe County District School Board Elementary School in Bradford West Gwillimbury, Ontario and 3 kilometres away from his birthplace, Bond Head, Ontario.
- Osler Library of the History of Medicine, McGill University, Montreal. Osler left his 8000 volume collection of books on the history of medicine to his alma mater. The library now holds over 100,000 volumes and is Canada's de facto 'national library of the history of medicine'.
- Promenade Sir-William-Osler (Formerly the upper section of rue Drummond.) adjacent to the campus of McGill University in Montreal, Quebec and leading to the McIntyre Medical Sciences Building, which houses the Osler Library of the History of Medicine.
- William Osler Health System 1998 near Brampton, Ontario
- Osler House is the student mess for clinical medical students of Oxford University and is found at the John Radcliffe Hospital in Oxford.
- Osler House is also the name of the old Observer's House, next to the Radcliffe Observatory in Green Templeton College, Oxford, a Grade I listed building.[45]
- Osler House is one of the two undergraduate hostels of the JIPMER medical school in Puducherry, India.
- Osler Textbook Room 1999 at Johns Hopkins Hospital[46] in the room in the Billings Building where Osler wrote 'Principles and Practice of Medicine'. It houses a collection of Osler memorabilia.
- Osler Center for Clinical Excellence 2002[47] devoted to teaching 'the basic elements of a sound doctor patient relationship'.
- Osler Hall is Dining Hall at Trinity College School, Port Hope, Ontario.
- Osler Hall is Main Hall of 'Med Chi' or Medical and Chirurgical Faculty, the Maryland State Medical Society,[48] located on Cathedral Street in Baltimore. The Med Chi House of Delegates meets and deliberates in Osler Hall wherein hang numerous portraits of famous Maryland physicians including a large portrait of Osler.
- Osler House (a medical residence) in Townsville, Queensland, Australia is believed to be named after him [49]
Awards[edit]
- American Association for the History of medicine, William Osler Medal.[50][51]
- Osler Library, McGill University. Pam and Rolando Del Maestro William Osler Medical Students Essay Awards.[52]
- Osler Lecture at the Worshipful Society of Apothecaries.[53]
- Student Award in Oslerian Medicine[54]
References[edit]
- ^Johns Hopkins Medicine: The Four Founding Professors. Hopkinsmedicine.org. Retrieved on May 30, 2014.
- ^ abTuteur, Amy (November 19, 2008). 'Listen to your patient'. The Skeptical OB. Archived from the original on March 19, 2012. Retrieved April 9, 2012.
- ^Markel, Howard (July 3, 2012). An Anatomy of Addiction. New York: Pantheon Books. p. 202. ISBN978-1400078790.
- ^Penelope., Hunting (2002). The history of the Royal Society of Medicine. London: Royal Society of Medicine Press. ISBN978-1853154973. OCLC47271565.
- ^Bryan, Charles; Fransiszyn, Marilyn. 'Osler usque ad mare: the SS William Osler'(PDF). CMAJ. 7: 849–852.
- ^Bliss, Michael (1999). William Osler: a life in medicine. Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press. p. 12 ISBN978-0-19-512346-3. OCLC41439631.
- ^Bliss, Michael (1999). William Osler: a life in medicine. Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press. p. 37 ISBN978-0-19-512346-3. OCLC41439631.
- ^Joseph Hanaway, '(1996). 'McGill Medicine: The First Half Century, 1829–1885. McGill-Queen's Press. p. 179
- ^Bliss, Michael (1999). William Osler: a life in medicine. Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press. p. 44 ISBN978-0-19-512346-3. OCLC41439631.
- ^Sir William Osler. The Quotable Osler. ACP Press. p.283 ISBN9781934465004
- ^Osler, William (2008). edited by Mark E. Silverman, T. J. Murray, Charles S. Bryan. The Quotable Osler. ACP Press. p. 284
- ^Bliss, Michael (1999). William Osler: a life in medicine. Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press. p. 45-46 ISBN978-0-19-512346-3. OCLC41439631.
- ^AEQUANIMITAS. Medicalarchives.jhmi.edu. Retrieved on May 30, 2014.
- ^Sokol, Daniel (November 17, 2007). 'Aequanimitas'. BMJ : British Medical Journal. 335 (7628): 1049.2–1049. doi:10.1136/bmj.39385.642315.FA. ISSN0959-8138. PMC2078638.
- ^Fisher, Kimberly A. 'History of The Johns Hopkins Hospital'. Retrieved February 19, 2017.
- ^James, D. G. (1992). 'The portraiture of Sir William Osler'. Postgraduate Medical Journal. 68 (797): 159. doi:10.1136/pgmj.68.797.159. PMC2399241.
- ^'Honours to Medical Men: Coronation Honours'. Lancet. 178 (4609): 1874. 1911. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(01)58188-x.
Sir William Osler, Regius professor of medicine in the University of Oxford, who is famous throughout two continents, has enriched the literature of medicine with many works of high scientific and literary value.
- ^'Sir William Osler Press Clippings 1905–1920'. National Library of Medicine.
- ^'Sir William Osler Collection, P100'. McGill Archival Collections Catalogue. Retrieved November 18, 2018.
- ^'Aequanimitas - Books and Men'. www.medicalarchives.jhmi.edu.
- ^Bibliotheca Osleriana. Mqup.mcgill.ca. Retrieved on May 30, 2014.
- ^Smith, Bernie Todd (July 1974). 'Marcia Crocker Noyes, Medical Librarian: The Shaping of a Career *'. Bulletin of the Medical Library Association. 62 (3): 314–324. ISSN0025-7338. PMC198800. PMID4619344.
- ^Crawford DS (2004). 'The Medical Library Association of Great Britain and Ireland'. Health Info Libr J. 21 (4): 266–8. doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2004.00533.x. PMID15606885.
- ^'The Bibliographical Society – Past Presidents'. Bibsoc.org.uk. November 18, 2008. Archived from the original on August 4, 2009. Retrieved January 24, 2011.
- ^(See Osler Library Studies in the History of Medicine vol. 8.)
- ^Golden, Richard (2004) A History of William Osler's The Principles and Practice of Medicine. Osler Library, McGill University. ISBN0-7717-0615-4.
- ^Bloodletting – UCLA Biomedical Library History and Special Collections for the SciencesArchived March 13, 2012, at the Wayback Machine. Library.ucla.edu. Retrieved on May 30, 2014.
- ^Journal of Perinatology (September 6, 2007). 'Access : Avicenna (AD 980 to 1037) and the care of the newborn infant and breastfeeding : Journal of Perinatology'. Journal of Perinatology. Nature. 28 (1): 3–6. doi:10.1038/sj.jp.7211832. PMID17805338.
- ^'William Osler and The Fixed Period: Conflicting Medical and Popular Ideas About Old Age'. ResearchGate. Retrieved February 18, 2019.
- ^Davis, Egerton Yorrick (1999). Golden, Richard L (ed.). The Works of Egerton Yorrick Davis, MD: Sir William Osler's Alter Ego. Osler Library studies in the history of medicine, no. 3. Montreal: Osler Library, McGill University. ISBN978-0-7717-0548-9. OCLC48551127. A collection of writings by the fictitious surgical character created by Osler, E.Y. Davis
- ^ ab'Egerton Y. Davis', Chris Nickson, Life in the Fastlane, November 16, 2008
- ^Wrong O (2003). 'Osler and my father'. J R Soc Med. 96 (6): 462–64. doi:10.1258/jrsm.96.9.462. PMC539606. PMID12949207.
- ^'Page Not Found - The Western Front Association'. www.westernfrontassociation.com.
- ^Starling, P H (March 2003). 'The case of Edward Revere Osler'. Journal of the Royal Army Medical Corps. 149 (1): 27–29. doi:10.1136/jramc-149-01-05. PMID12743923.
- ^ abBliss, Michael (1999). William Osler: a life in medicine. Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN978-0-19-512346-3. OCLC41439631.
- ^'Grace Revere Osler. A Brief Memoir'. Journal of the American Medical Association. 97 (13): 954. September 26, 1931. doi:10.1001/jama.1931.02730130058045. ISSN0002-9955.
- ^'They Put Their Brains To Work William Osler, Joseph Leidy, Edward Drinker Cope And William Pepper Were Among The Greatest Brains In Turn -of-the-century Philadelphia. And They Still Are'. Articles.philly.com (April 3, 1991). Retrieved on May 30, 2014.
- ^Osler Library Newsletter No. 60 February 1989Archived July 5, 2013, at the Wayback Machine. mcgill.ca
- ^Cushing, Harvey (1925). The Life of Sir William Osler. Oxford: Clarendon Press. OCLC268160.
- ^'Sir William Osler'. Canadian Medical Hall of Fame. Archived from the original on May 26, 2011. Retrieved March 24, 2010.
- ^'William Osler and his Gulstonian Lectures on malignant endocarditis'. ResearchGate. Retrieved February 18, 2019.
- ^'11 Facts About Sir William Osler'. Stanford Medicine 25. Retrieved February 18, 2019.
- ^'Sir William Osler High School – Welcome to Sir William Osler High School'. Tdsb.on.ca. June 10, 2010. Retrieved January 24, 2011.
- ^SWO.scdsb.on.ca. SWO.scdsb.on.ca (May 4, 2014). Retrieved on May 30, 2014.
- ^Historic England. 'Osler House (1369464)'. National Heritage List for England. Retrieved February 14, 2017.
- ^The Osler Textbook Room. Medicalarchives.jhmi.edu. Retrieved on May 30, 2014.
- ^Hopkinsbayview.org. Hopkinsbayview.org (June 24, 2011). Retrieved on May 30, 2014.
- ^Medchi.org. Medchi.org (April 8, 2014). Retrieved on May 30, 2014.
- ^'Osler House (entry 600931)'. Queensland Heritage Register. Queensland Heritage Council. Retrieved August 1, 2014.
- ^'William Osler Medal American Association for the History of Medicine'. www.histmed.org. Retrieved July 28, 2017.
- ^'Competitions Pritzker School of Medicine The University of Chicago'. pritzker.uchicago.edu. Retrieved July 28, 2017.
- ^'Pam and Rolando Del Maestro William Osler Medical Students Essay Awards McGill Library - McGill University'. www.mcgill.ca. Retrieved July 28, 2017.
- ^'Osler Lecture'. www.apothecaries.org.
- ^'Student Award in Oslerian Medicine UTMB Health UTMB.edu'. www.utmb.edu. Retrieved July 28, 2017.
Bibliography[edit]
| Library resources about William Osler |
| By William Osler |
|---|
- Celebrating the Contributions of William Osler. Alan Mason Chesney Medical Archives 1999. Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions.
- Famous Canadian Physicians: Sir William Osler at Library and Archives Canada.
- Osler, William (1969) [1929]. Francis, William W; Hill, Reginald H; Malloch, Archibald (eds.). Bibliotheca Osleriana: A Catalogue of Books Illustrating the History of Medicine and Science (Revised ed.). Montreal: McGill-Queen's University Press. ISBN978-0-7735-9050-2. OCLC75916. The Introduction and other editorial matter is freely available on-line.
- Osler, William; Silverman, Mark E; Murray, T J; Bryan, Charles S (2002). The Quotable Osler. Philadelphia: American College of Physicians. ISBN978-1-930513-34-1. OCLC50477294.
- 'Sir WILLIAM OSLER Bt., M.D., F.R.S., F.R.C.P'. British Medical Journal. 1 (3079): 30–33. January 3, 1920. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.3079.30. PMC2337064.
External links[edit]
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: William Osler |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to William Osler. |
- https://profiles.nlm.nih.gov/GF/ Sir William Osler in the US National Library of Medicine's 'Profiles in Science'
- Richard L. Golden; Charles G. Roland (1988). Sir William Osler. Norman Publishing. ISBN978-0-930405-00-7.
- Sir William Osler Archival Collection at the Osler Library of the History of Medicine, McGill University
- William Osler Letter Index, Osler Library of the History of Medicine
- Roland, Charles G. (1998). 'Osler, Sir William'. In Cook, Ramsay; Hamelin, Jean (eds.). Dictionary of Canadian Biography. XIV (1911–1920) (online ed.). University of Toronto Press.
- William Osler Photo Collection, Osler Library of the History of Medicine
- Works by William Osler at Project Gutenberg
- Works by or about William Osler at Internet Archive
- Works by William Osler at LibriVox (public domain audiobooks)
- Aequanimitas from the Alan Mason Chesney Medical Archives of the Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions.
- [1] at 13 Norham Gardens, owned by Sir William Osler while Regius Professor of Medicine at Oxford University (information from Green Templeton College, Oxford)
- Osler House Club, Oxford University
- Osler biography, chronology, bibliography & resources (from Johns Hopkins)
- Murray, T. Jock (January 2009). 'Read any good books lately?'. McGill J Med. 12 (1): 90–91. PMC2687923. PMID19753296; Osler's bedside table Library for Medical Students